Micron resolution particle image velocimetry (Micro-PIV) is a tool for measuring the velocity profile across a plane in a microfluidic device. Because of the small dimensions of the flow field in micro channel flow, it is impossible to use conventional PIV systems to obtain two orthogonal planes for optical access to the flow field. Instead, micro PIV systems use a volume illumination technique where the light source and the view field are introduced through the same optics. With this approach the focal plane is moved down through the flow field to map the entire volume.

ÁPIV (and PIV) is a whole-field, non-intrusive measurement technique where the fluid velocity is measured by recording the displacement of small tracer particles added to the fluid. A single PIV measurement produces a velocity vector field of high spatial resolution. The technique is based on the following simple principle: Consider a single particle in a fluid flow. The particle is assumed to have the same density as the surrounding fluid, and a size small enough so that the particle follows the flow faithfully without influencing the fow itself. Next, record the position x of the particle in two time instants separated by a short time interval dt.
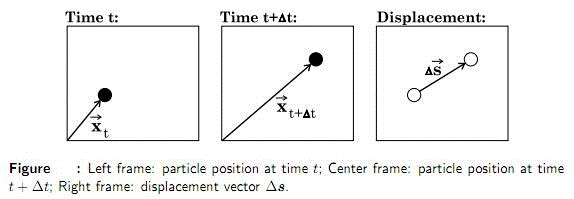
If dt is sufficiently short, the displacement of the particle, ds, is small enough so that the direction and magnitude of the particle velocity during dt can be assumed constant, i.e. the acceleration is negligible. Then the local fluid velocity may be estimated as:
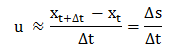
The simple idea described above can now be extended to an entire flow field. In PIV, the working fluid is seeded with small tracer particles, and the flow field of interest is illuminated by a powerful light source, most often a laser. The light scattered or emitted by the particles (particle images) is then recorded on film or CCD array at two different time instants separated by dt. As a single image pair contains hundreds or thousands of particles, the images are divided into small subareas, so-called interrogation regions. Each region is analyzed by some correlation method in order to find the local displacement vector ds, and calculate the velocity vector field.
Courtesy:
1. Micro-PIV and its application to some BioMEMS related micro fluidic flows, Michal M. Mielnik, Department of Energy and Process Engineering, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim Norway
2. Department of Plama and Laser Applications
3. University of Sheffield Department of Chemical and Process Engineering







